SAP Access Control: Unlock Smarter Security with Attribute-Based Access (ABAC)
Introduction
As your company’s digital footprint grows, effective SAP access control becomes mission-critical. Relying on static roles alone leaves your system vulnerable especially when managing Segregation of Duties (SoD), remote access, and exception-heavy workflows.
The good news? You don’t have to choose between flexibility and security.
By complementing traditional SAP Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) with Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC), you can move from reactive to proactive — preventing violations in real-time, not after the fact.
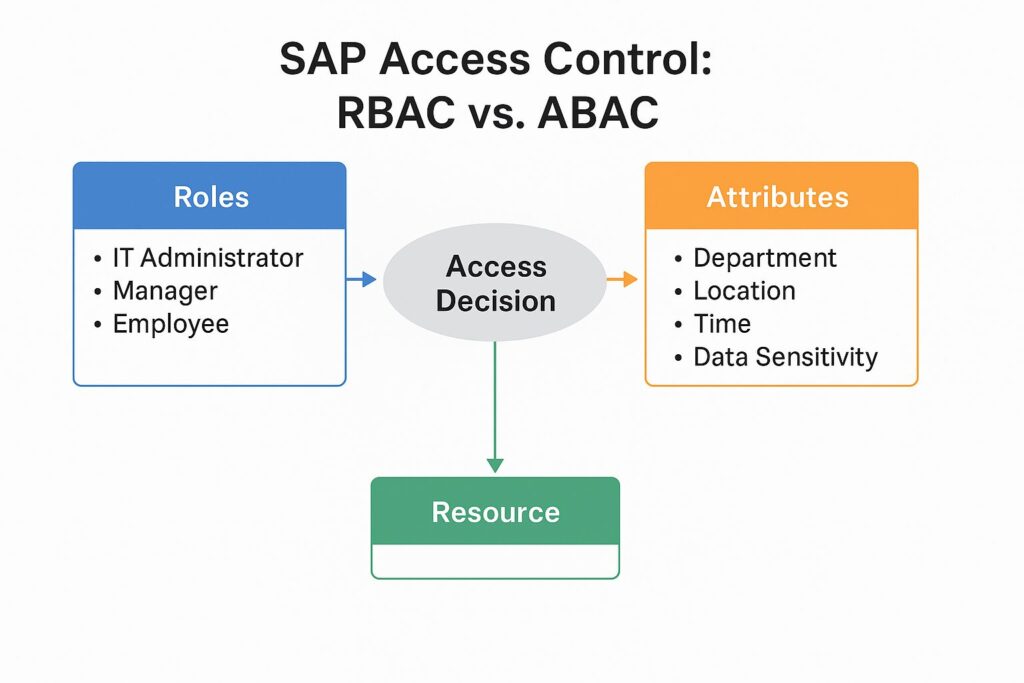
🔐 Understanding SAP Access Control Using Roles
In SAP, roles define what users can see and do. Functionally, they are collections of permissions that align access to job responsibilities and enforce the principle of “need to know.”
RBAC involves three core elements:
- Role assignment – Only authorized users are granted access.
- Role authorization – Permissions are explicitly tied to those roles.
- Transaction authorization – Users can only perform approved transactions within their assigned roles.
Over time, SAP evolved RBAC to include hierarchies. Executives might inherit access from department heads and team leaders. However, while efficient, this model lacks the granularity needed for dynamic, exception-heavy operations.
🛠️ Why RBAC Alone Isn’t Enough in Modern SAP Landscapes
RBAC was built for static, on-prem environments — not today’s dynamic, cloud-first, hybrid-access ecosystems. It’s binary: you either have access or you don’t.
But business requirements have changed. Employees work remotely, handle cross-functional responsibilities, and often need exceptions to get work done. When SoD conflicts arise, RBAC doesn’t know why or how a role is being used — just that a transaction is allowed.
This is where traditional SAP access control falls short.
💡 Enhancing SAP Access Control with ABAC
Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC) extends RBAC by introducing dynamic conditions into the access decision.
Think of attributes as context:
- User attributes: Department, job level, citizenship, clearance
- Action attributes: Read, write, approve, transfer
- Resource attributes: Document type, transaction code, classification
- Environment attributes: Time of day, IP address, device, location
By combining these in real-time, SAP systems can evaluate not just who the user is — but whether they should be doing something under current conditions.
✅ Real-World Example: Why ABAC Matters
Let’s say an IT administrator has full access to modify the user database. In an RBAC model, that person can do so anytime, from anywhere.
With ABAC, we can define:
If the admin is working from home (environment attribute),
they can only read the database (action attribute).
But if they log in between 8 AM and 10 AM on weekdays,
they can edit user data — and only within HR-related tables.
This creates intelligent, time- and context-bound access — reducing risk without impeding productivity.
🔄 Hybrid SAP Access Control: RBAC + ABAC for Modern Enterprises
The future of SAP security lies in layered access control. RBAC remains the foundation, defining the what. ABAC defines the how, when, and under what conditions.
Together, they enable:
- Fine-grained control over sensitive operations
- Dynamic SoD enforcement based on actual business context
- Reduced false positives in GRC/audit reports
- Greater agility for exception handling
- Real-time risk mitigation without user friction
🧨 The Cost of Not Adopting ABAC in SAP
Without ABAC, companies resort to:
- Creating excessive custom roles for each exception
- Over-granting access and hoping logs will catch misuse
- Spending hours manually reviewing SoD violations
This is not scalable. It’s not secure. And it doesn’t meet modern compliance standards.
🛡️ Enterprise Data Insight: Powering Dynamic SAP Access Control
At Enterprise Data Insight, we help organizations transition from rigid role models to dynamic, real-time access enforcement with our solution — Dynamic Data Enforcement (DDE).
Built to work natively with SAP ECC and S/4HANA, DDE:
- Evaluates user, document, and environment attributes on the fly
- Blocks risky transactions before they happen
- Logs every access decision for full audit transparency
Whether you’re mitigating SoD risk or enabling secure exceptions, DDE brings true ABAC to SAP.
✅ Conclusion: Secure More, Grant Smarter
SAP access control is no longer just about granting roles. It’s about making smart, real-time decisions that adapt to your business context.
With ABAC, you’re not just controlling access — you’re controlling risk.
👉 Learn how to bring ABAC to your SAP landscape with Enterprise Data Insight’s Dynamic Data Enforcement:
🌐 www.edatainsight.com


